Understanding the different types of computer memory
Computer memory plays a crucial role in the performance and functionality of every computer system. It is responsible for storing and retrieving data, allowing for quick and efficient access. There are several different types of computer memory, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes. In this article, we will explore the various types of computer memory and their functions.
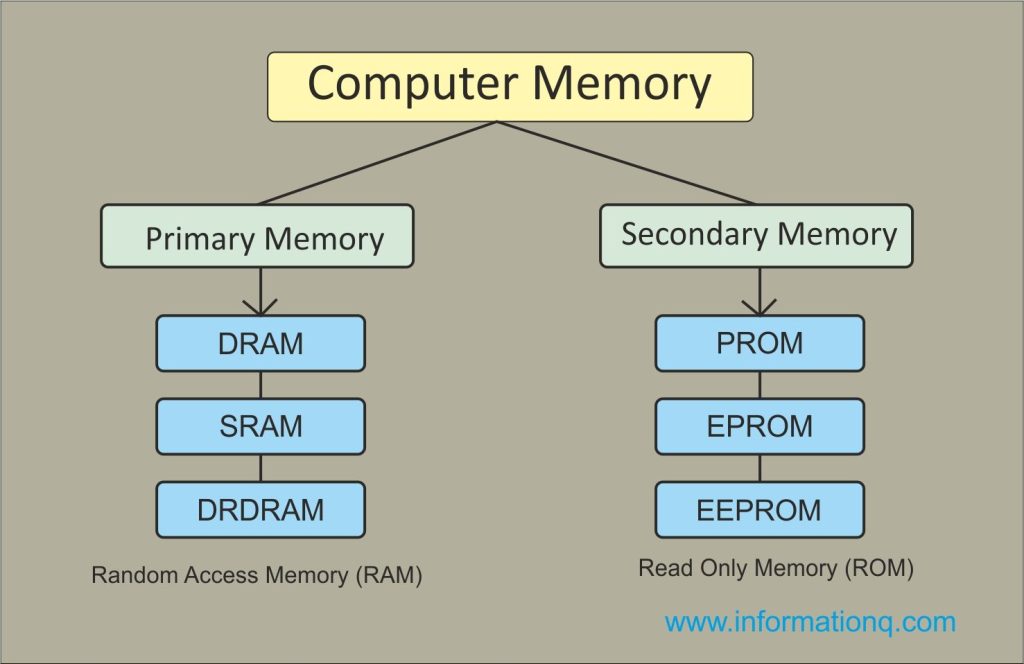
1. Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM is a type of volatile memory that provides temporary storage for data that is actively used by the computer’s operating system, software applications, and user tasks. It enables quick access to data, allowing for smooth multitasking and efficient program execution. However, RAM does not retain data once the computer is powered off or restarted.
2. Read-Only Memory (ROM)
ROM is a type of non-volatile memory that permanently stores instructions necessary for booting up the computer and initializing hardware components. It contains firmware or software that cannot be altered or erased by normal computer operations. ROM ensures that essential system instructions are always accessible, even if the computer loses power.
3. Cache Memory
Cache memory is a small, high-speed memory component that stores frequently accessed instructions and data for faster retrieval. It works as a buffer between the CPU and RAM, reducing memory latency and alleviating the load on the main memory. Cache memory is critical for improving overall system performance and reducing bottlenecks.
4. Virtual Memory
Virtual memory is a combination of RAM and secondary storage (typically the hard disk drive) that provides an extension to the computer’s physical memory. It allows the computer to run larger programs and handle more complex tasks by temporarily transferring less frequently used data from RAM to the hard disk. This frees up space in RAM for more urgent tasks, effectively expanding the available memory.
5. Flash Memory
Flash memory is a popular type of non-volatile memory commonly used in devices like USB drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and memory cards. It stores data in cells made of floating-gate transistors and does not require a constant power supply to retain data. Flash memory is known for its durability, speed, and low power consumption.
6. Magnetic Storage (Hard Disk Drives)
Hard disk drives (HDDs) are magnetic storage devices that use rotating platters and magnetic heads to read and write data. They offer large storage capacities, making them suitable for long-term data storage. HDDs are commonly used in desktop computers, laptops, and servers due to their cost-effectiveness and reliability.
7. Optical Storage (CDs/DVDs/Blu-ray)
Optical storage devices, such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs, store data using lasers to read and write microscopic pits on the disc’s surface. They are commonly used for distributing software, movies, and music. While optical storage provides a convenient way to store and share data, it has lower storage capacities compared to magnetic storage.
Conclusion
Computer memory is a vital component that enables smooth and efficient operation of computer systems. Understanding the different types of computer memory, such as RAM, ROM, cache memory, virtual memory, flash memory, magnetic storage (HDDs), and optical storage, allows users to make informed decisions when it comes to memory requirements and storage needs for their devices. Each memory type serves a specific purpose, contributing to the overall performance and functionality of the system.